From electronic health records to practice management tools and telemedicine apps, today’s healthcare software handles an enormous amount of patient data every day. While these digital tools are essential to centralize medical records and reduce paperwork, they are also vulnerable to costly data breaches and cybersecurity risks.
According to a HIPAA journal report, nearly 275 million healthcare records were exposed in 2024, representing an alarming rise over previous years. This surge underscores the need to ensure robust data security and HIPAA compliance in healthcare software. Without proper safeguards, every connected system, whether used for appointment scheduling or remote monitoring, can become an entry point for attackers. Healthcare providers and organizations can invest in professional medical software development services to build systems that stay fully compliant with HIPAA regulations and other regulatory standards.
Why Data Security Matters in Modern Healthcare Software
Modern healthcare relies heavily on digital platforms to manage appointments, lab results, prescriptions, and virtual consultations. As these systems grow more interconnected, the volume and sensitivity of data moving across them increase. This makes strong data security essential to support safe and uninterrupted patient care while ensuring compliance with regulatory systems. Here are the key reasons organizations should prioritize healthcare cybersecurity in their digital systems:
- Healthcare is a top target for threat actors: Cybercriminals often target healthcare data because it contains highly valuable personal, medical, and financial information. This makes hospitals and clinics highly susceptible to attacks such as ransomware, phishing, and unauthorized access attempts that can disrupt critical services.
- Data breaches carry serious consequences: When patient information is exposed or altered, healthcare organizations face legal action, hefty penalties, and long recovery periods. Beyond financial impact, compromised data can lead to delayed treatments, incorrect medical decisions, and a loss of trust among patients.
- Interconnected systems increase vulnerabilities: Most practices now rely on interconnected platforms such as EHRs, telehealth apps, pharmacy systems, and diagnostic tools. If even one component has weak security, it can put the entire network at risk and create multiple entry points for attackers.
- Compliance failures can halt operations: Lack of proper security controls and failure to meet HIPAA standards can result in audits, corrective action plans, and restrictions on system usage. This disrupts workflows and limits a provider’s ability to deliver seamless care.
Strong health IT security measures are not only a compliance requirement but also foundational for safe, ethical, and reliable care delivery. With rising threats and higher expectations for digital transparency, securing medical software is no longer optional but a necessity for every medical organization.
Common Vulnerabilities in Healthcare IT Systems
Despite significant advancements in digital health, many healthcare systems still operate with gaps that expose sensitive information to unauthorized access. These weaknesses often arise from outdated tools, inconsistent security practices, or overreliance on third party technologies. Identifying these healthcare software vulnerabilities is the first step to strengthening overall data protection.
- Outdated or unpatched software: Many healthcare organizations rely on legacy systems that may no longer receive regular updates. Without timely patches, these platforms become easy targets for attackers who exploit known security flaws. This creates persistent cybersecurity risks that can spread across the entire network.
- Weak authentication and access controls: Simple passwords, shared logins, and poorly managed user roles allow unauthorized individuals to enter critical systems. When access permissions are not regularly reviewed, employees may retain privileges they no longer need. This increases the chances of accidental or intentional misuse of patient data.
- Lack of encryption: When data is stored or transmitted without proper encryption, it becomes readable to anyone who intercepts it. This creates a high risk during file transfers, cloud storage, and communication between connected devices. Without strong encryption protocols, even routine workflows can expose sensitive patient information to unauthorized access
- Insufficient API and integration security: Modern healthcare software often connects with billing platforms, pharmacies, labs, and third party apps. If these APIs are not secured properly, they can act as hidden pathways for intruders.
- Human errors and untrained staff: Employees who lack cybersecurity awareness may fall for phishing attempts or mishandle sensitive files. Accidental data exposures are common when staff are not trained on secure practices, as around 20% of healthcare organizations were reported to fall victim to cloud misconfiguration attacks. These everyday mistakes can open doors for more serious breaches.
These vulnerabilities show how easily healthcare systems can be compromised when security is not continuously monitored and updated. Addressing these gaps early supports stronger compliance and builds a safer digital environment for patient care.
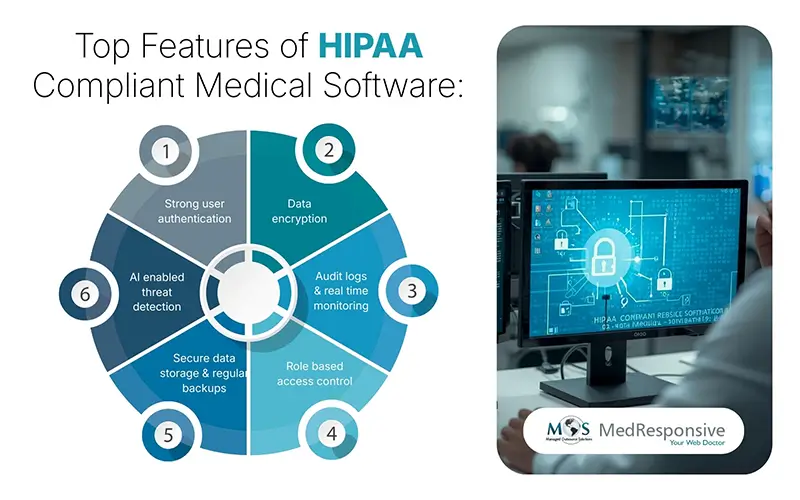
Key Features of HIPAA-Compliant Medical Software
HIPAA-compliant medical software must be built with strong technical safeguards that protect patient data at every stage of its lifecycle. These features ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information and that all activity within the system is monitored and secured. Here are the key features that healthcare companies should consider when implementing software:
- Strong user authentication: Authentication methods such as multi factor login, biometrics, or one time codes ensure that only verified users can access protected data. These controls help prevent unauthorized logins, especially in high risk environments. Consistent authentication policies reduce exposure to both internal and external threats.
- Data encryption: Encryption protects patient information during storage and while it is being transferred between devices or systems. Even if data is intercepted, encrypted files remain unreadable without the correct decryption keys. This adds an essential layer of defense against cyberattacks targeting medical communications and cloud storage.
- Audit logs and real time monitoring: Every access attempt, system change, or data view must be tracked through detailed audit trails. These logs help identify misuse, suspicious activity, or compliance violations. Real time monitoring tools alert administrators to unusual behavior so that threats can be contained quickly.
- Role-based access control: Role-based permissions ensure that employees only view information relevant to their responsibilities. This prevents unnecessary exposure of sensitive data and limits the damage even if an account is compromised. Regularly updating roles helps maintain a clean, compliant access structure.
- Secure data storage and regular backups: HIPAA-compliant systems store data in protected environments with encryption, redundancy, and strict access policies. Routine backups ensure operational continuity even during outages, ransomware attacks, or system failures. This helps organizations recover quickly without losing vital patient information.
- AI enabled threat detection: Modern healthcare software integrates AI tools that identify patterns, detect unusual access behavior, and signal potential security breaches. These systems analyze large volumes of activity data to flag suspicious events faster than manual monitoring. AI enhances compliance by reducing response time and strengthening overall cybersecurity risk management in healthcare.
Software that incorporates these features creates a more controlled, transparent, and secure environment for managing patient data. As cyber risks evolve, these capabilities ensure that companies can maintain robust protection while meeting HIPAA standards.
Best Practices for Healthcare Software Data Security
Maintaining HIPAA compliance is not a one-time task but an ongoing commitment that requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and improvement. Strong security practices help healthcare organizations stay resilient against new threats and ensure that patient information is handled responsibly at every stage.
These practices given below create a stable foundation for safe and compliant digital operations:
- Conduct regular risk assessments: Ongoing risk assessments help identify vulnerabilities across software, workflows, and third party tools. By reviewing potential threats proactively, organizations can put corrective measures in place before problems escalate. This approach ensures compliance gaps are caught early and managed effectively.
- Train employees on security protocols: Human error is one of the leading causes of data breaches, so consistent training is essential. Staff should be highly trained to recognize phishing attempts, handle sensitive information, and follow secure access practices. Regular training also helps to keep everyone aligned with evolving healthcare compliance requirements.
- Use secure hosting and reliable cloud infrastructure: HIPAA-compliant hosting environments provide safeguards such as encryption, access control, backups, and audit logs. Choosing a certified cloud provider ensures that patient data is stored and processed securely. This reduces risk while supporting more scalable and efficient software performance.
- Develop incident response plan: Practices and clinics need a clear plan that outlines what happens when a security issue affects their software. This includes steps to identify the problem quickly, secure affected systems, switch to safe backups, and notify the required teams. A well-rehearsed plan helps minimize disruption to patient care and ensures the organization meets HIPAA reporting requirements.
- Perform routine compliance and security audits: Regular internal and external audits help evaluate how well systems adhere to HIPAA regulations. Audits reveal outdated processes, configuration gaps, and overlooked risks that could lead to violations. Addressing these findings promptly keeps software aligned with regulatory standards.
Applying these practices consistently will help companies stay compliant while reducing the risk of costly breaches or regulatory penalties.
Reach Out to a Trusted Specialist
As digital care expands, practices must stay vigilant about how information is collected, stored, and processed by their digital systems. Developing HIPAA-compliant medical software in-house can be highly complex, requiring specialized expertise in cybersecurity. Healthcare brands can partner with a reliable medical software development company to ensure their systems meet HIPAA requirements, implement strong security measures, and support smooth clinical workflows.
Experts understand the complexities of secure healthcare data management and they can tailor solutions to the specific needs of your practice. By collaborating with trusted specialists, healthcare teams can confidently adopt technology that is secure, efficient, and fully compliant.