Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have emerged as a vital component in healthcare technologies, revolutionizing how patient data is stored, managed, and accessed. As technology continues to advance, EHRs will likely play an even more significant role in transforming healthcare businesses and improving the overall quality of care.
EHR application development offers numerous benefits for businesses in the healthcare sector, such as –
- Enhanced patient care
- Improved communication and collaboration
- Reduced errors and improved patient safety
- Efficient information retrieval
- Streamlined workflows
- Cost savings
- Revenue cycle management
- Patient engagement and empowerment
- Scalability and growth
According to a report from Grand View Research, the global electronic health records market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 4.1% from 2023 to 2030 to reach USD 38.5 billion by 2030. A significant increase in the demand for electronic health records due to the growing digitalization and rising demand for centralization and streamlining of healthcare administration are key factors that are driving the market for electronic health records.
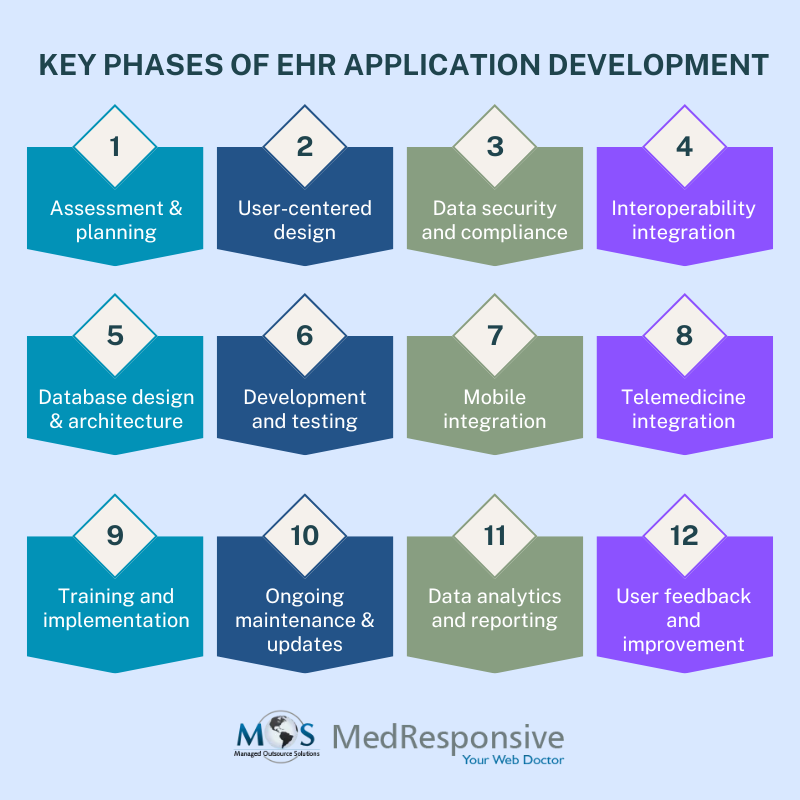
Navigating the Key Phases of EHR Application Development
Each stage in EHR application development, from initial assessment to ongoing improvement, plays a critical role in the success of the system.
- Assessment and planning: The journey of EHR development begins with a thorough assessment. Healthcare providers must identify their specific requirements and objectives. This stage involves evaluating the existing systems, understanding workflow processes, and soliciting input from clinicians and staff. The planning phase sets the foundation for the entire development process by defining goals, scope, and resources.
- User-centered design: One of the most critical aspects of application development is ensuring a user-friendly interface. Developers must collaborate closely with healthcare professionals to design an intuitive system that aligns with clinical workflows. Usability testing and feedback loops are integral to refining the user experience, making it efficient and easy for healthcare providers to use.
- Data security and compliance: The system must adhere to strict regulatory standards such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) to protect patient information. Developers need to implement robust encryption, access controls, and audit trails to maintain data integrity and patient privacy.
- Interoperability integration: Healthcare systems rely on data exchange between various providers and systems. Developers must work on incorporating standard protocols like HL7 (Health Level Seven) and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) to enable seamless data sharing between different EHR platforms.
- Database design and architecture: EHR systems deal with vast amounts of data. Choosing the right database design and architecture is crucial for scalability and performance. Developers need to decide whether to use relational databases or NoSQL databases, considering factors like data volume and transaction speed.
- Development and testing: The actual development of the EHR system involves coding and implementing the planned features. It’s essential to follow Agile or DevOps methodologies to ensure iterative development and quick adaptation to changing requirements. Rigorous testing, including unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing, are critical to identify and rectify issues early in the development process.
- Mobile integration: In today’s healthcare landscape, mobility is key. EHR systems should extend their reach through mobile applications, allowing healthcare providers to access patient data on the go. Mobile integration requires careful consideration of security and usability, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected.
- Telemedicine integration: Telemedicine gained immense prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic. This prominence could continue. EHR systems should be equipped to seamlessly integrate with telehealth platforms, enabling remote consultations and remote monitoring of patients. This integration enhances patient care and accessibility.
- Training and implementation: Successful EHR implementation requires comprehensive training for healthcare staff. Developers and healthcare organizations must collaborate to provide training sessions and resources to ensure that end-users can effectively utilize the system without disruption to patient care.
- Ongoing maintenance and updates: EHR application development doesn’t end with implementation. Continuous maintenance and updates are critical to address bugs, security vulnerabilities, and evolving regulatory requirements. Developers should establish a robust system for monitoring and responding to issues promptly.
- Data analytics and reporting: EHR systems generate vast amounts of data that can be harnessed for clinical decision support, population health management, and research. Integrating data analytics tools and reporting features into the EHR system is essential for healthcare providers to make informed decisions and improve patient outcomes.
- User feedback and improvement: Feedback from healthcare providers and end-users is invaluable. Developers should establish mechanisms for gathering user feedback and regularly incorporate improvements and enhancements to meet changing needs.
Development of EHR/EMR application is a complex and dynamic process that plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare. Developers, healthcare organizations, and end-users must collaborate closely to ensure that these stages are navigated effectively, resulting in a robust, secure, and user-friendly EHR system that ultimately enhances patient care and outcomes.
At MedResponsive, we successfully converted a legacy 80s DOS-based program into a cloud-based application with a focus on EHR development.