It may not be surprising these days how Google seems to know exactly what we are thinking about when it presents search results; regardless of whether we are looking for a nearby cafe or a complex scientific formula. It all comes down to the magic of the search engine giant’s revolutionary algorithm. The history of Google algorithm is fascinating.
As you may have heard, Rome wasn’t built in a day.
Yes. This magic wasn’t conjured up in a day (or night). In fact, the Google algorithm evolution happened over two decades, in an attempt to figure out how to display and rank results exactly in the way we want.
Let us now take a journey through time to figure out how Google algorithm evolved over the years to make Google the most sophisticated search engine that we all rely upon so much.
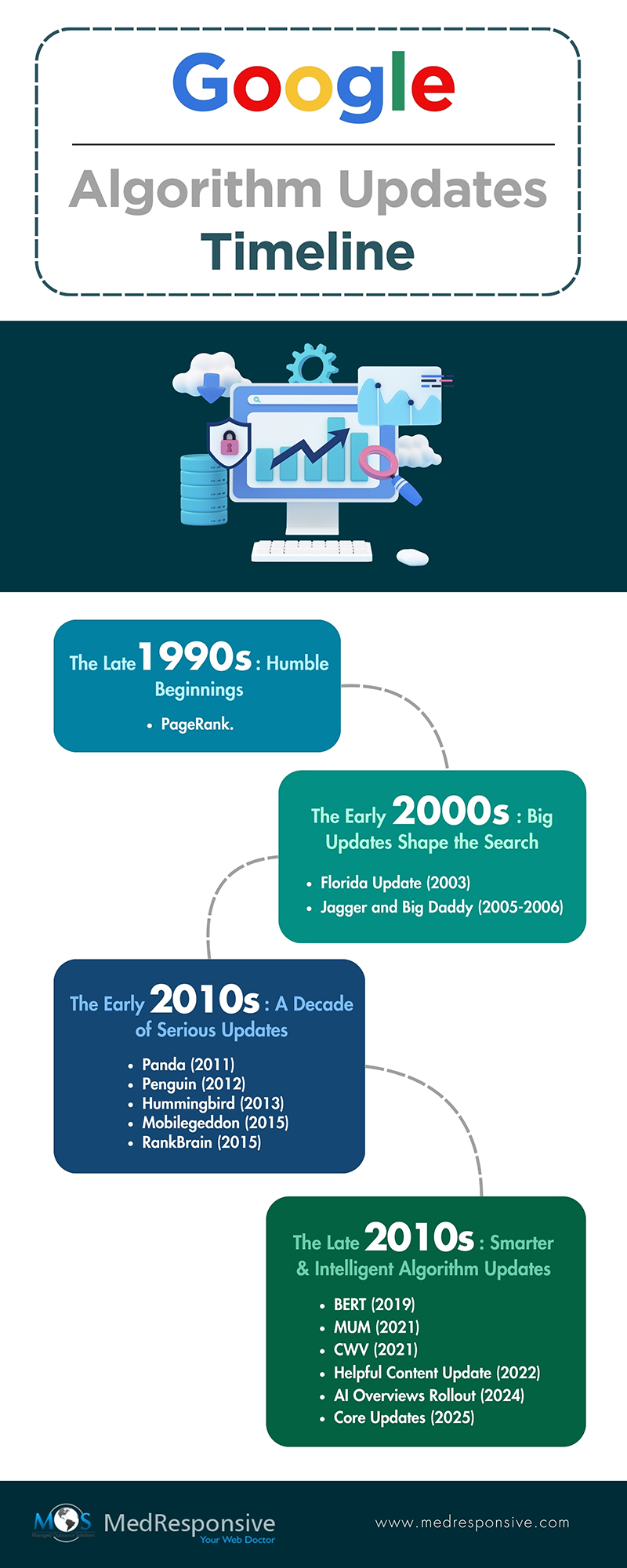
The Late 1990s: Humble Beginnings
In 1996, Larry Page and Sergey Brin—two Stanford PhD students—developed a search engine called, “Backrub.”
Yup, Backrub.
They named it so because it analyzed the web’s “back links” to understand how important a website was, and what other sites it was related to. The name stuck on for a year, before a graduate student Sean Anderson suggested the term, “googolplex” and Page shortened it to Googol. They then accidentally searched for the term, “Google.com” whilst looking for a domain name to register, which eventually Page liked and they registered it in the Fall of ‘97.
Anyhow, that’s the history regarding how the name came into place.
Regarding the first major breakthrough, it was around a year later when Google’s core algorithm was built on a simple, but revolutionary idea: PageRank.
PageRank algorithm analyzed the number and quality of links that were pointed to a page, which was used to determine its significance. The logic was simple: if other websites were linking to a page, it must be valuable.
This was revolutionary, compared to other search engines of the time, which ranked results based on the number of keywords on the page. Google delivered relevant results almost all the time. However, it was far from perfect. Foxy webmasters exploited the system through keyword stuffing and link farms, which called for an urgent revamp of the present algorithm.
The Early 2000s: Big Updates Shape the Search
With the start of the millennium, post the dot-com boom and crash, the digital landscape was going through a violent shakeup, and so was Google. While many dot-com startups and peers faced shut down, Google in an attempt to stay afloat, refined its algorithm through a series of updates which would later not just redefine the future of the company, but the Web itself.
- Florida Update (2003): This first update was Google’s big attempt to squash spamming. All of a sudden, websites that stuffed keywords in their pages and relied on hidden text were penalized. Many business owners faced the heat, but it opened up the way for websites that presented cleaner and more user-friendly content.
- Jagger and Big Daddy (2005-2006): These updates targeted websites with low-quality backlinks, thereby prioritizing link quality rather than quantity. Those websites that had either purchased links or had deployed some unethical practices saw their rankings stoop, signaling a clear message: integrity mattered in search.
The Early 2010s: A Decade of Serious Updates
With the internet exploding into the mainstream channels, tons of content filling the Web each day, search behaviors started to evolve which also meant Google had to get smarter with its algorithm. This decade saw the most significant Google algorithm updates in SEO history, reshaping how enterprises approached search engine optimization.
- Panda (2011): The Panda update was the start of a turning point. It identified and lowered the rankings of low-quality, less content and rewarded high-quality, useful content. Basically, if your website was a treasure trove of valuable content, it would be promoted up the ranks. But if your content was poorly written, Panda was not your friend.
- Penguin (2012): Google, tired of spammy backlinks, introduced the Penguin update. This update hammered on manipulative link-building practices (which was a norm back then) and rewarded websites that followed organic link-building practices. It basically forced SEOs to focus on earning links naturally rather than staking the system.
- Hummingbird (2013): Google introduced semantic search through the Hummingbird update, focusing on user intent rather than on a bunch of relevant keywords. This integration enabled the algorithm to better understand what the user would be thinking, allowing it to process complex queries and display results more effectively.
- Mobilegeddon (2015): With the widespread adoption of smartphones in the early 2010s, mobile browsing became the norm, which made Google include mobile-friendliness as a ranking factor. Those websites that weren’t optimized for mobile devices were put down the ladder, ensuring users always had a better browsing experience.
- RankBrain (2015): This update was the game changing moment with Google, as it took its first real steps into Artificial Intelligence. RankBrain, an AI-powered system, enabled Google to process search queries more effectively, as it was trained to understand nuanced language and hence deliver more accurate results, especially for ambiguous or long-tail searches.
The Late 2010s – Early 2020s: Smarter & More Intelligent Algorithm Updates
Artificial Intelligence has revolutionized Google’s algorithm updates like never before. The series of Google AI search updates have transformed search results from responding to what you type to predicting what you’d need.
- BERT (2019): Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), could be termed as the more polished version of RankBrain, brought on for understanding natural language. It enabled the search engine to understand the context of complex queries—context, subtle nuances and prepositions. For example, when a user types, “European traveler needs a US visa”, BERT understands that an European traveler is planning to travel to the US and is looking for how and where to apply for a visa.
- MUM (2021): MUM (Multitask Unified Model) was an update that took things a further notch ahead, enabling Google to process and interpret information across multiple languages in video, audio and image simultaneously. It’s designed to answer complex queries that require nuanced understanding and provides more relevant and accurate information.
- CWV (2021): Core Web Vitals (CWV) was an update that solely focused on improving user experience through metrics like a website’s loading speed, visual stability and interactivity. Websites that met these criteria were rewarded with higher rankings, demonstrating Google’s effort in prioritizing user experience and satisfaction.
- Helpful Content Update (2022): Google’s Helpful Content Update is sending out a clear message: content created with the sole purpose of increasing rankings, is not going to cut it. The search engine instead will be valuing websites that provide genuine and informative content to its users, thereby aligning with their mission of making valuable information universally accessible.
- AI Overviews Rollout (2024): In 2024, Google transformed search with the rollout of AI Overviews, which use generative AI to deliver direct, context-aware answers at the top of SERPs. This shifted SEO from simply ranking pages to earning visibility through authority and structure. Websites with deep expertise, clear content organization, and strong trust signals became more likely to be referenced and cited by AI, rather than just clicked.
- Core Updates (2025): Google’s core updates pushed search toward a predictive, intent-led model, predicting user needs instead of reacting to queries. Search systems improved at handling multi-step exploration and aligned AI Overviews more closely with organic results. Content that supports decision-making, credibility, and usability became central to long-term visibility in an answer-driven search ecosystem.
Key Takeaways That Still Hold True
Content is King, has always been the King and will stay the King.
Across every major algorithm evolution, one principle remains unchanged: Google consistently rewards websites that prioritize users over tactics.
Therefore, to stay competitive:
- Create content that demonstrates real expertise and first-hand experience
- Design websites that are fast, intuitive, and accessible
- Build topical authority instead of stuffing keywords
While black-hat or shortcut SEO tactics may give you short-lived gains, Google’s increasingly intelligent systems ensure that long-term visibility belongs only to clean, user-first strategies.
If navigating these updates feels too much, collaborating with an expert provider of SEO consulting services like MedResponsive can make a decisive difference. With deep technical expertise and healthcare-focused SEO experience, MedResponsive helps identify underlying issues, align content with modern search expectations, and build sustainable growth—without risking penalties.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Google Search & SEO
Google’s algorithm evolution reflects more than technical advancement—it mirrors how people search, think, and make decisions online.
From keyword matching to intent understanding, from ranking pages to generating answers, search has become smarter, more contextual, and increasingly human-like.
For businesses and marketers, the path forward is clear:
- Stop optimizing for algorithms
- Start optimizing with users in mind
By understanding how Google has evolved (and why) it becomes far easier to future-proof your SEO strategy and stay ahead in an AI-driven search landscape.
The future of search isn’t something to fear. It’s something to align with and grow alongside.